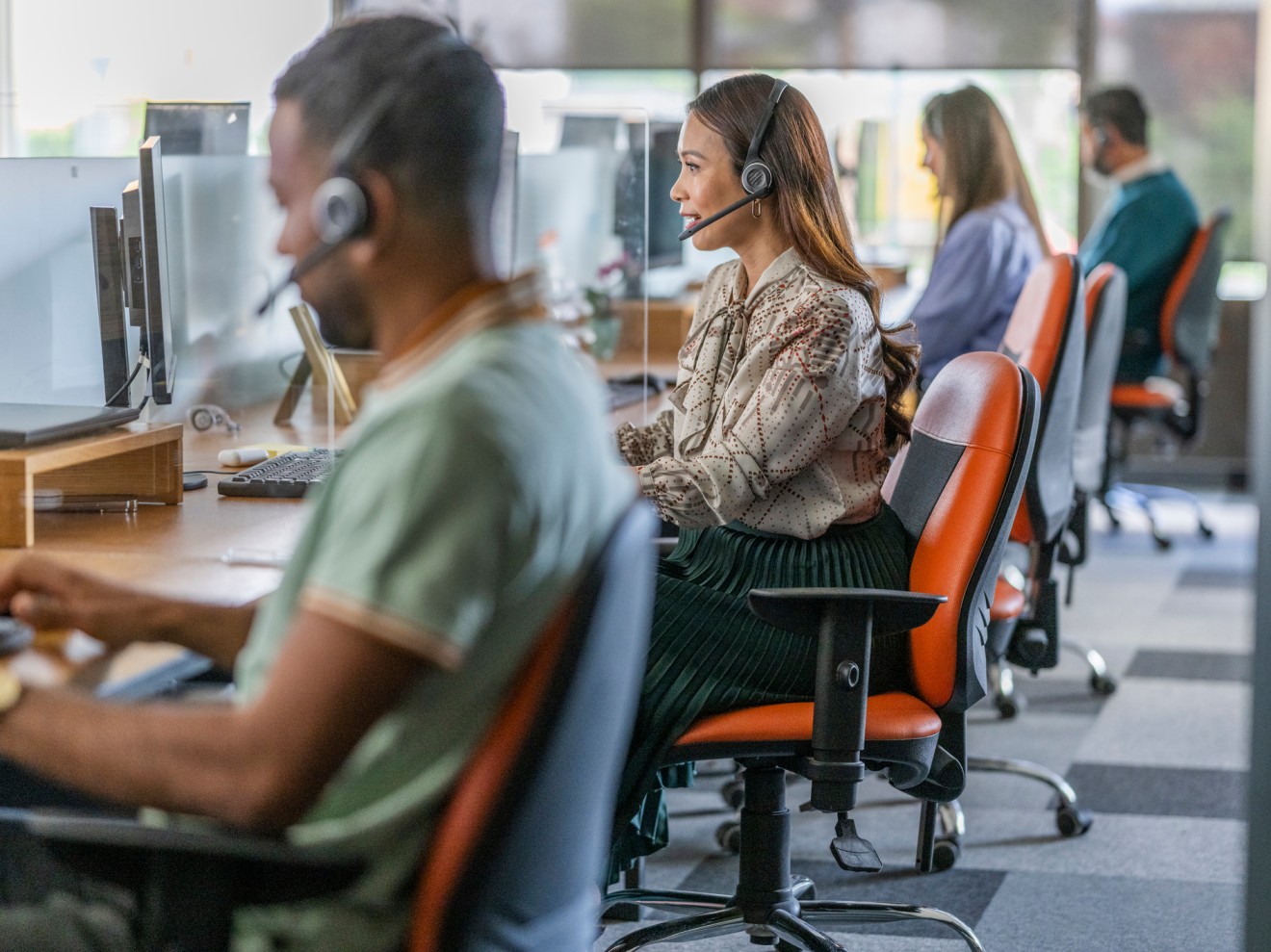
Call center authentication helps protect customers and organizations by verifying identities while minimizing friction. This guide summarizes proven approaches for call center customer authentication, covers technical and operational controls and provides a practical roadmap for deploying adaptive, privacy-first solutions that help reduce fraud and improve customer experience.
What Is Call Center Authentication?
Call center authentication is the process of confirming a caller’s identity before revealing sensitive data or allowing account changes. Modern approaches move beyond rote knowledge-based checks to a mix of passive, active, biometric and token-based techniques that together form resilient call center customer authentication.
Effective authentication balances security with speed to keep average handle time low while preventing account takeover and social engineering attacks.
Why Caller Authentication Matters
Robust caller authentication best practices help to reduce fraud, regulatory exposure and reputational risk. Poor or outdated caller verification procedures provide fraudsters with the opportunity to exploit weak knowledge-based authentication checks and impersonation, resulting in potential financial loss and customer churn.
Strong call center customer authentication builds customer trust by showing that the organization handles personal data seriously and is prepared to stop misuse before it escalates.
Call Center Authentication Process and Flows
A repeatable call center authentication flow simplifies design and training. Typical stages include:
- Initiation: includes IVR prompts, ANI checks and branded calling to establish a trusted call channel
- Verification: passive signals (device intelligence, voiceprint matching) and active checks (one-time passcodes, FIDO2 passkeys) as risk dictates.
- Decision: handled by a rules engine that either approves the caller, challenges for additional factors or routes to a specialist team.
- Fallback: flows should be secure and provide clear agent scripts for edge cases to avoid inconsistent handling and CX degradation.
Call Authentication Core Methods
Call center authentication best practices suggest using multiple complementary technologies rather than a single control.
- Multi-factor authentication and password-less options: Combine something a caller knows with something they have or are. Password-less flows such as FIDO2 passkeys reduce shared-secret risk and simplify caller verification during agent-assisted sessions.
- Voice biometrics and other biometric checks: Voiceprint recognition can authenticate callers during the call without interrupting conversation, improving both security and experience. Combine voice biometrics with liveness and anti-spoofing checks to counter recordings and deepfakes.
- Behavioral and passive authentication: Analyze voice dynamics, call metadata, device signals and historical behavior to create a continuous risk score. Passive measures let you authenticate silently for low-risk requests and escalate only when anomalies appear.
- Knowledge-based authentication (KBA): Use dynamic, transaction-specific questions rather than static facts; treat KBA as a secondary layer, not the sole control.
- Telephony-specific checks: ANI matching, caller ID verification, STIR/SHAKEN anti-spoofing and caller verification services help identify spoofed numbers and reduce impersonation risk.
Call Center Authentication Best Practices
1. Layered and Adaptive Authentication Strategy
Design call authentication strategies as adaptive orchestrations that adjust friction to the risk level. Implement a call authentication rules engine that:
- Applies passive checks first to preserve CX.
- Triggers active, stronger factors for higher-value transactions or anomalous signals.
- Uses contextual signals (geography, device fingerprint, recent activity) to score risk.
- Records decisions and outcomes to refine thresholds over time.
A layered call authentication approach – combining passive voiceprints, device signals, MFA or passkeys, and telephony verification – provides in-depth call center security while keeping straightforward calls fast.
2. Implementation Roadmap and Integrations
To follow best practices when implementing call center authentication, follow a phased rollout to reduce disruption and prove the value.
- Assess current state: map existing IVR, CRM and agent desktop integrations; capture baseline KPIs like average call authentication time, false-positive rate and fraud incidents.
- Pilot passive authentication: deploy voice biometrics and behavioral signals in monitoring-only mode to establish baseline accuracy.
- Integrate systems: connect call authentication services with CRM, IVR and agent workflows via APIs so identity context is available in the agent desktop.
- Add active controls selectively: introduce MFA or passkeys for high-risk transactions and self-service changes.
- Monitor and iterate: use analytics to tune thresholds, reduce false positives and lower friction.
Key integrations include:
- CRM for context-aware routing
- IVR for capture and deflection
- Analytics platforms for continuous improvement
3. Operational Playbooks and Training
Technology alone is not enough to implement a strong call center authentication strategy. Call center fraud prevention and call center security relies on technology paired with robust operations and training.
Call center authentication best practices suggest documenting clear agent procedures and maintaining ongoing training.
- Create scripts for call authentication failures, escalation to manual review and customer education during challenging caller verification.
- Train agents to spot social engineering cues and to follow consistent caller verification playbooks.
- Implement runbooks for fraud incidents, including short-term containment and post-incident reconciliation.
- Track operational metrics: call authentication success rate, time to authenticate, number of escalations, customer effort score and call center fraud prevention outcomes.
Regular tabletop exercises and simulations help teams stay sharp and reveal gaps in both process and tooling.
4. Technology Selection Criteria
Choosing the right call center authentication solutions that align with security, UX and operational needs will ultimately impact the results that your call center sees. When it comes to selecting the best call center authentication solution for your business, TNS suggest considering the following to inform your decision:
- Security Features: support for MFA, voice biometrics with anti-spoofing, behavioral risk scoring and telephony anti-spoofing (STIR/SHAKEN).
- UX Features: silent/passive authentication, password-less options, branded calling to improve call trust and minimal challenge interruptions.
- Integration and Scalability: APIs for CRM, IVR and agent desktop; support for cloud telephony and hybrid deployments.
- Compliance and Privacy: strong encryption, data minimization, consent controls and certifications relevant to your geography and sector.
- Vendor Reliability: SLAs, call center fraud detection performance and clear product roadmaps.
Call center authentication best practices recommend prioritizing platforms that allow phased adoption so call center authentication can start with low-friction measures and add stronger controls as needed.
5. Compliance, Privacy and Data Security
Call center security, compliance and privacy are all of vital importance. To ensure that all areas are protected and compliance is adhered to, call center authentication best practices suggest:
- Handle biometrics and identity signals with care.
- Encrypt data at rest and in transit, apply strict access controls and retain only the data you need for the minimal time required.
- Ensure your approach meets regulatory requirements for your industry and regions, such as PCI-DSS for payments, GDPR for EU residents and sector-specific rules for healthcare.
- Transparently communicate authentication methods to customers and obtain consent where required.
6. Costs, Risk Management and Change Management
Lastly, understand the costs, the risk and the changes that will need to be impacted when rolling out a call center authentication strategy should be considered:
- Calculate total cost of ownership including licensing, integration, training and ongoing tuning.
- Balance these costs against fraud losses and the customer experience impact of high-friction solutions.
- Implement change management with stakeholder buy-in, measurable KPIs, and a phased rollout plan to limit disruption.
A Look to the Future
As technology evolves, so do threats to the voice channel. AI plays a dual role – faster, safer call authentication also enabling scams that bypass protection. To stay ahead, enterprises must anticipate risks like voice deepfakes and review risk models continuously. Protecting inbound calling operations is increasingly critical as threats like TDoS attacks and impersonation scams grow more sophisticated.
The future of call center authentication best practices lies in AI-driven passive biometrics, advanced anti-spoofing and adaptive orchestration. Password-less standards and passkeys will help combat contact center fraud while unified platforms integrating telephony signals, behavioral biometrics and identity orchestration will become the norm.
Effective call center authentication requires a layered approach that blends technology, process and people. By combining passive authentication, biometric checks, telephony anti-proofing and CRM/IVR integration, organizations can reduce call center fraud, protect customer data and maintain seamless experience for legitimate callers. Ongoing measurement, rule tuning and training updates are essential to keep pace with evolving threats and expectations.
TNS’ call center authentication solutions such as TNS Enterprise Authentication and Spoof Protection provide call center operators to achieve the desired effective call center authentication approach and help restore trust to the voice channel.
Mike Schinnerer is Vice President of Enterprise Product Management at TNS with specific responsibility for TNS Communications Market.
Discover TNS’ Authentication Solutions
Learn how TNS can help to improve your inbound and outbound calling operations and protect enterprises and customers.





